Gap Filler Liquids
(GFL)


What are gap filler liquids?
an explanation
Key Facts
to the GFLs from Kerafol®
- 2K system
- Mixing ratio 1:1
- Different polymer bases possible, silicone-containing and silicone-free
- Wide range of thermal conductivity (from 1.5 W/mK to 4.3 W/mK)
- High electrical insulation strength, from 10 kV/mm up to 20 kV/mm
- Curing at room temperature
- Heat-resistant, up to 200 °C
- Layer thickness from 50 µm to several mm possible
- Different designs in the area of thixotropy
- Highly thixotropic
- Self-levelling gap fillers (GFL 1800 SL and GFL 3000 SL) similar to potting materials
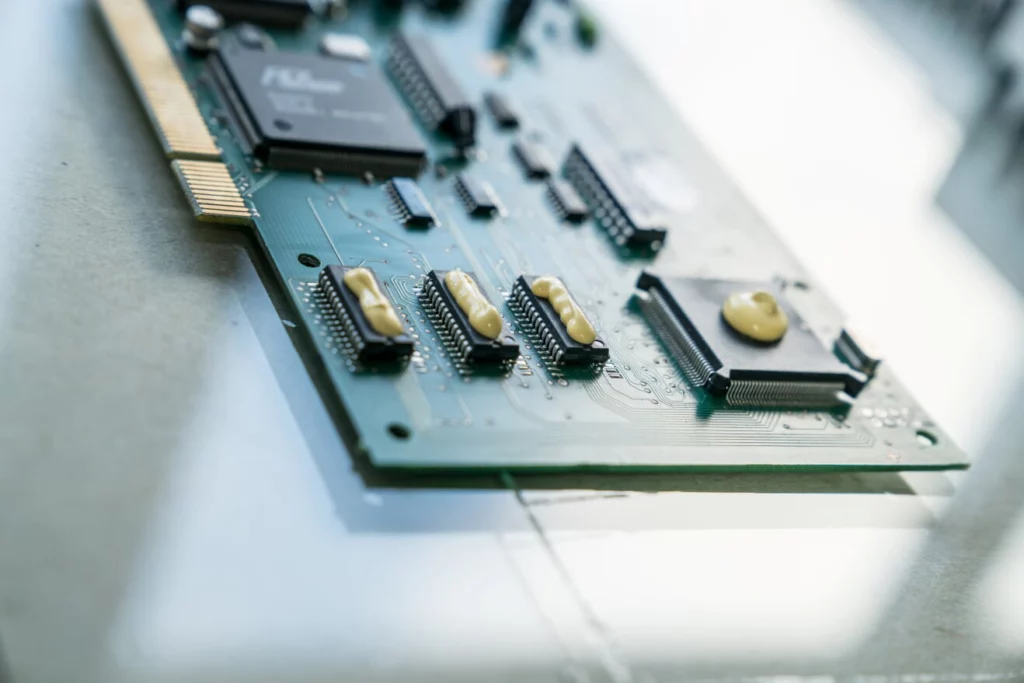

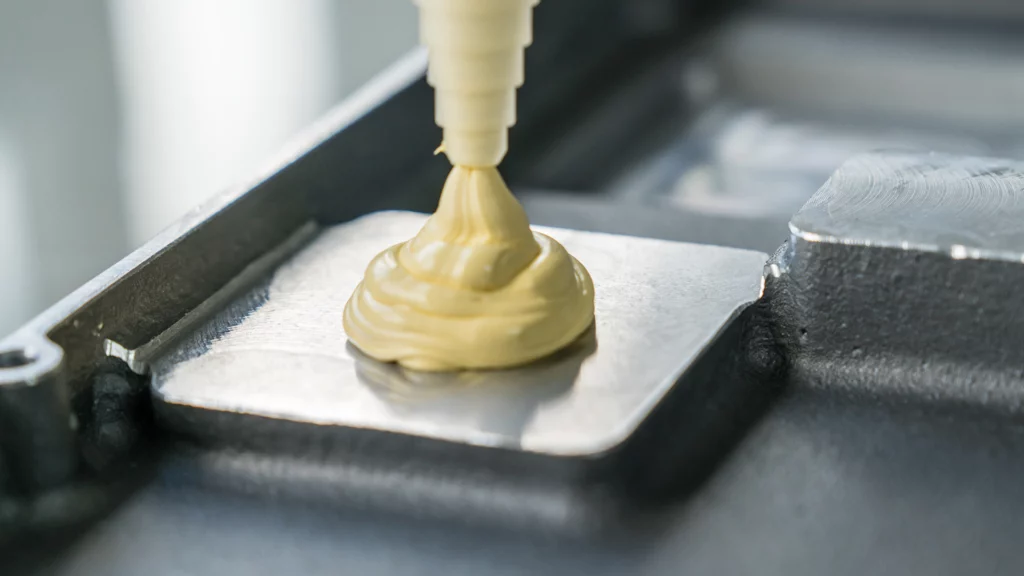
How are gap filler liquids processed?
Application
- Cartridges 50 ml / 200 ml / 400 ml / 1200 ml double cartridges
- Doses 0.5 kg / 1.0 kg doses
- Hobbocks up to 34.5 kg
In addition to manual application with pneumatic or electric dispensing guns (e.g. manufacturer/link), gap fillers can also be applied fully automatically using dispensing systems.
During application, it is always important to ensure that the two components are mixed homogeneously, which can be easily checked visually thanks to the color gradient.
Further information on dispensing technology and screen printing can be found in the section Service Kerafol.
Video: Application
Advantages
the GFL from Kerafol®
- Wide range of products for different requirement profiles
- High heat and long-term resistance
- Good adhesion and cohesion
- Low pressure required for compression due to "wet-on-wet installation", a great advantage especially for sensitive electronic applications
- Due to the low viscosity and the resulting good flow behavior, automation of the application (e.g. by dosing systems) can be implemented quite easily according to the state of the art
- High availability
- 100% Made in Germany
Delimitation
to other products
Gap filler liquids are cross-linking systems and therefore harden in contrast to heat-conducting pastes.
This makes them more robust and durable compared to pastes, especially under high mechanical loads such as vibrations or different expansion coefficients of the joining partners (keyword “CTI mismatch”).
After cross-linking, they have similar properties to a gap pad and take on the function of an elastomer due to their Shore 00 hardness.
The filling level and density of gap fillers is very high, and the choice of fillers is always based on the fact that they must be easy to dose.
In terms of the gap to be bridged over a certain area, gap fillers are a more cost-effective alternative than gap pads, also because the material utilization is higher (e.g. there is no material loss due to punching residues).
However, this is offset by the investment costs for a dosing system.

Comparison
Thermal Gap Filler Liquids from Kerafol®
Applications
from Gap Filler Liquids
- In many power electronics applications and many other electronic assemblies
- Batteries, busbars
- For high component tolerances / large gap dimensions
- Efficient solution, especially for higher quantities
- When automated component application is required

