Energy
Industry / Markets
Hydrogen technologies
The production of energy carriers based on renewable sources is an essential component of the energy transition towards a CO2-neutral and therefore climate-friendly energy economy.
Hydrogen plays a key role here, both as a substitute for fossil fuels and as a storage medium for electricity generated from renewable sources.
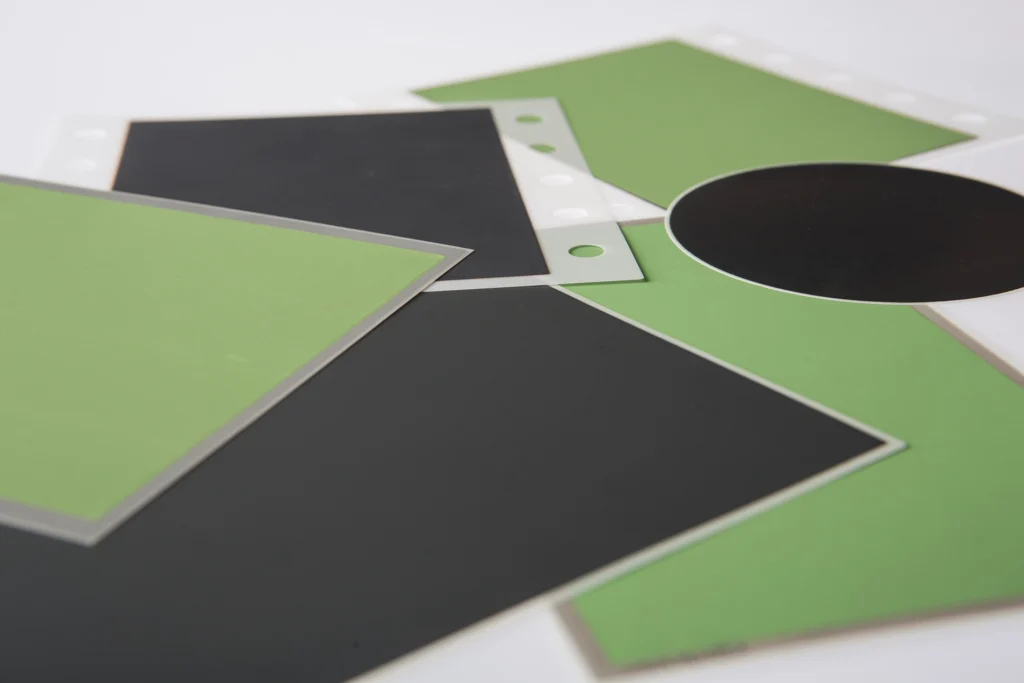


We manufacture zirconium oxide electrolytes for high-temperature fuel and electrolysis cells (solid oxide fuel/electrolysis cells – SOFC/SOEC), partial cells and complete cells, glass solders for joining stacks and special firing supports for sintering cells.
Solutions
for hydrogen technologies
Energy storage
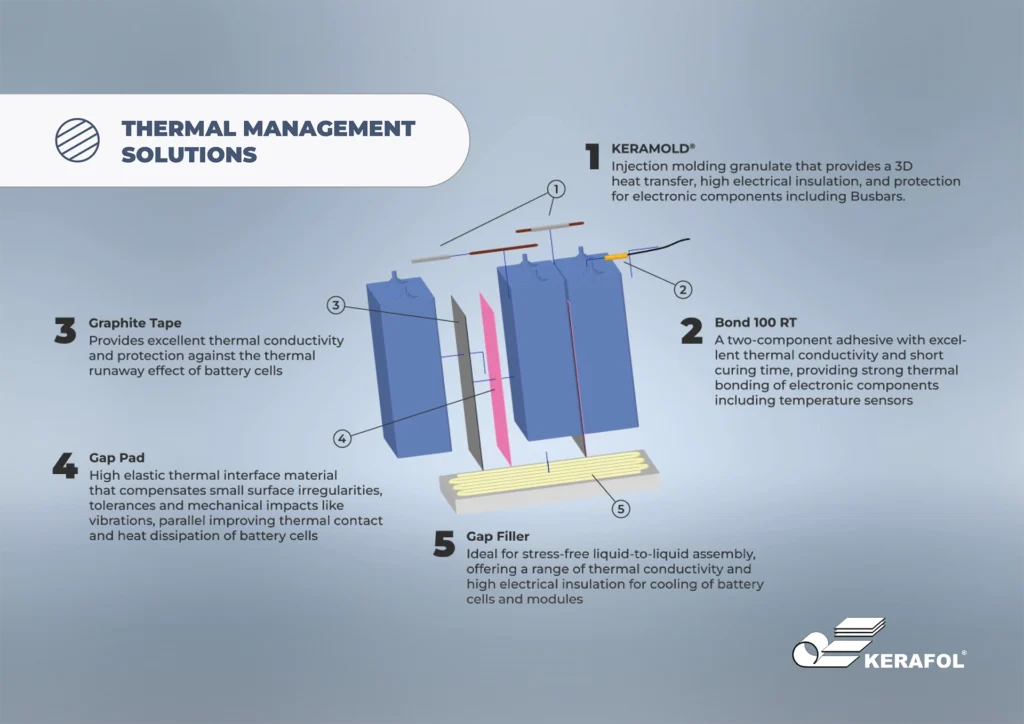
With the prevailing boom in batteries for electric and hybrid cars, the importance of stationary storage systems has long been neglected.
If the ever-increasing demand for electricity in the vehicle sector is to be covered by renewable energies, adequate and widely developed storage technology is required.
The functional principle is similar to that in the automotive sector, but the dimensions are significantly larger and the specific requirements and load profiles also differ.
While weight and various energy conversion processes play a major role in electric cars, stationary energy storage systems are primarily concerned with storing large amounts of electricity for longer periods of time and releasing it again when required.
This is particularly useful when using renewable energies in order to be able to absorb corresponding load peaks.
Currently, wind turbines have to be switched off for short periods of time to avoid overloading the grid.
This surplus electricity in particular can be stored using large battery containers or used to produce hydrogen by electrolysis.
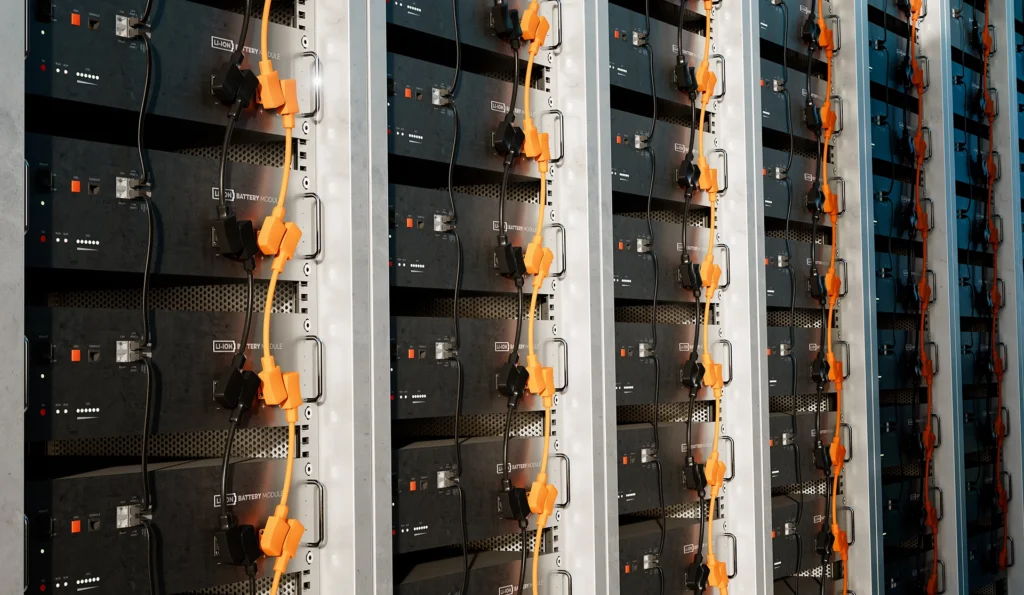

Solutions
for energy storage
Energy converter
Following strong growth in installed photovoltaic capacity, the expansion of PV systems in Germany has stalled since 2012.
Due to the goal of achieving C02-neutral electricity production, the rate of expansion has increased significantly again.
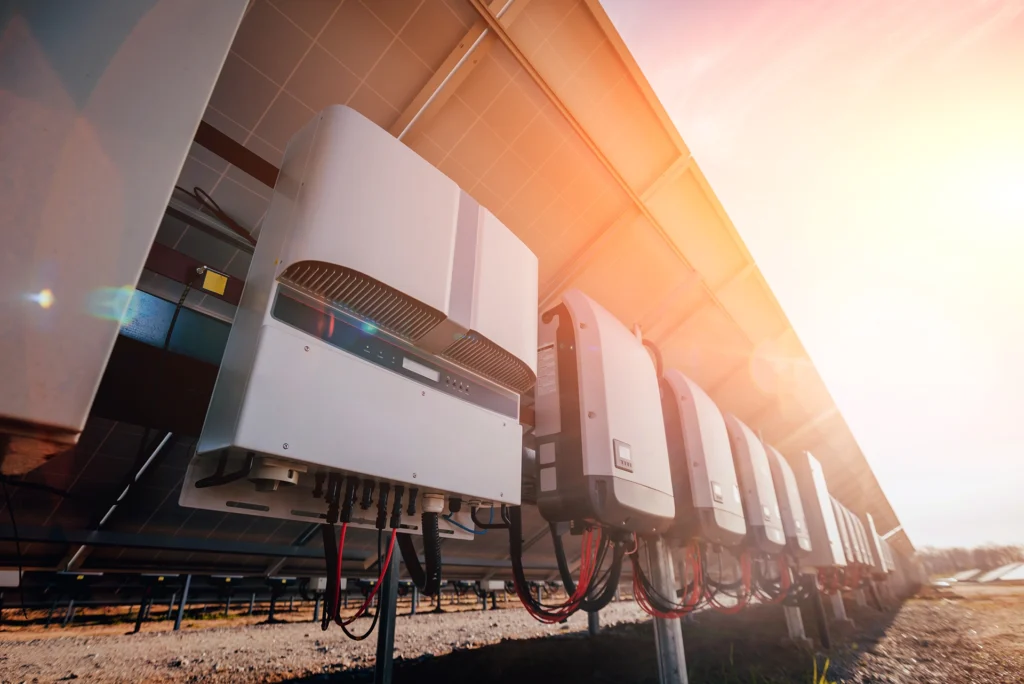
In addition to PV modules, so-called inverters or solar inverters are required to operate a system.
The solar cells used in PV modules generate direct current, whereas most electrical consumers require alternating current.
The inverter therefore takes on the task of making the electricity generated usable.
Good inverters use functions such as maximum power point tracking to ensure that the overall efficiency of the system is as high as possible.
The type of inverter required depends on the size of the photovoltaic system.
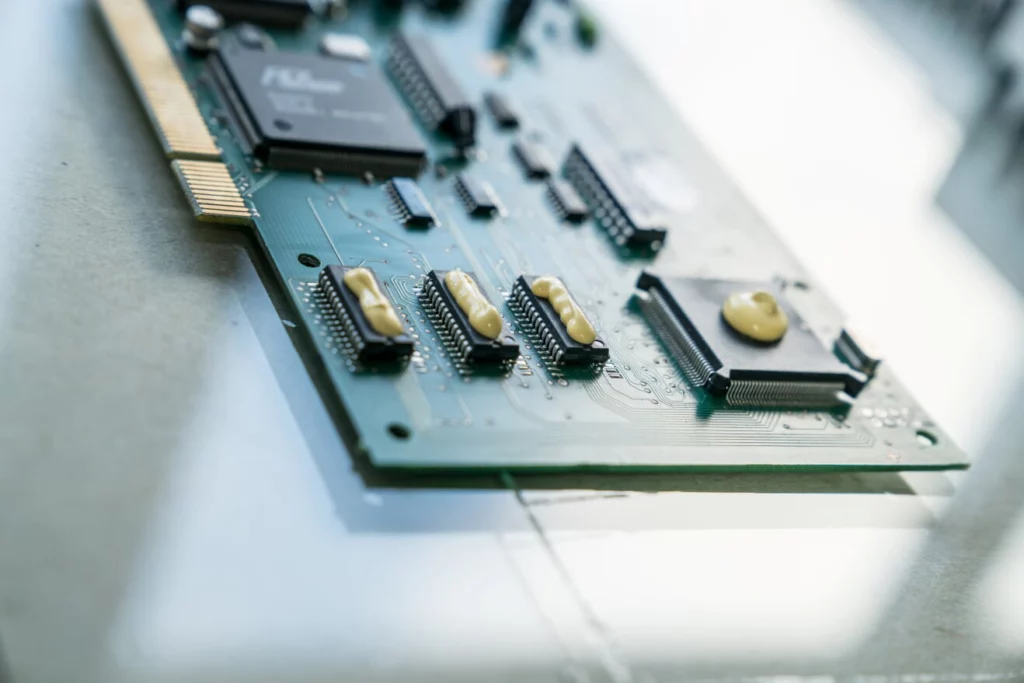
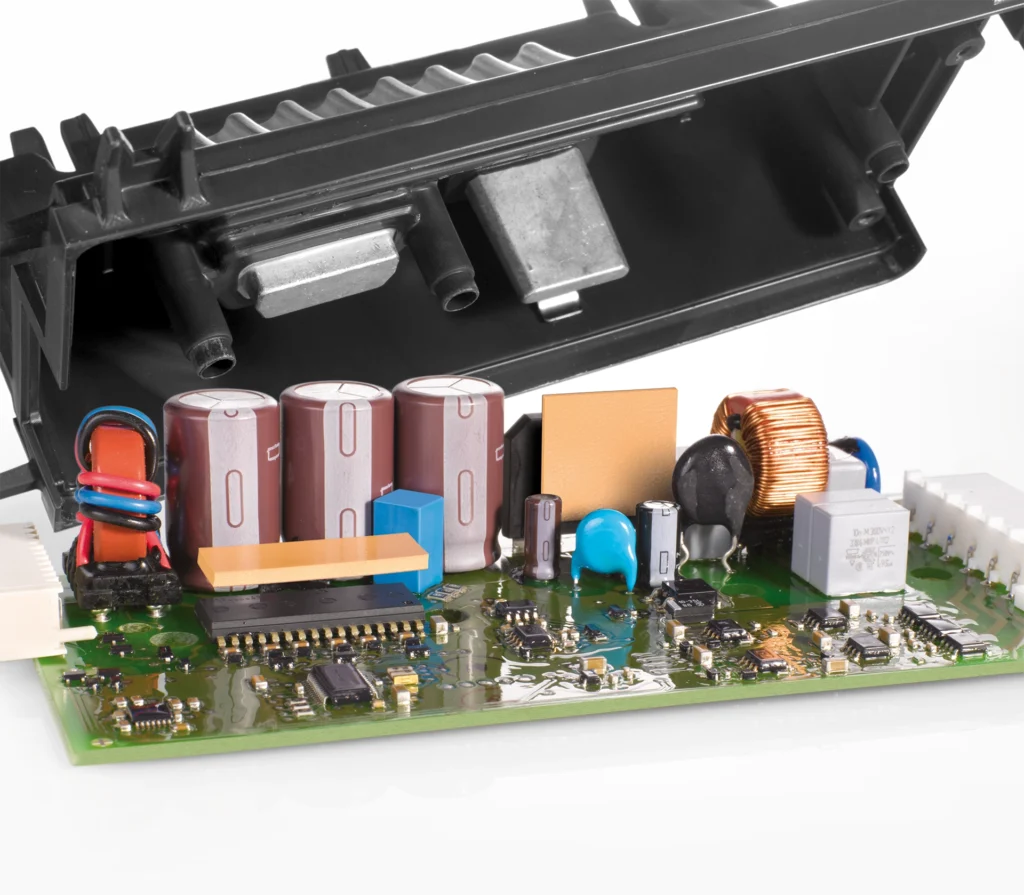
The electronic components installed in it are subject to high stress due to the many switching and conversion processes and heat up as a result.
So-called thermal interface materials (TIM) are used to conduct the heat from the heat source to the heat sink (e.g. metal housing or heat sink).


Solutions
for energy converters
Charging stations / Wallbox
The availability of charging points in particular is still a topic of discussion when it comes to purchasing a purely electrically powered vehicle.
The expansion of the charging infrastructure has been slow for a very long time, but new providers of charging technology and more efficient systems are leading to an improvement in charging options, both public and private.
While charging stations can only be found in public spaces, i.e. at petrol stations or service areas, wallboxes are often privately owned.
A wallbox and most charging stations work with alternating current.
A shorter charging time is possible with so-called fast charging stations.
With fast charging, the charging station itself converts the alternating current into direct current and passes this on to the battery of the electric car with minimal loss.
Most fast charging stations use the IU charging process: the battery is charged in phases in order to utilize the full charging capacity.
Charging is initially carried out using constant current until around 80 percent of the charging capacity is reached, which is possible within a very short time.
The charging station then switches to constant voltage.
The higher the charge level of the battery, the less current is supplied.
This prevents the battery from being overloaded.